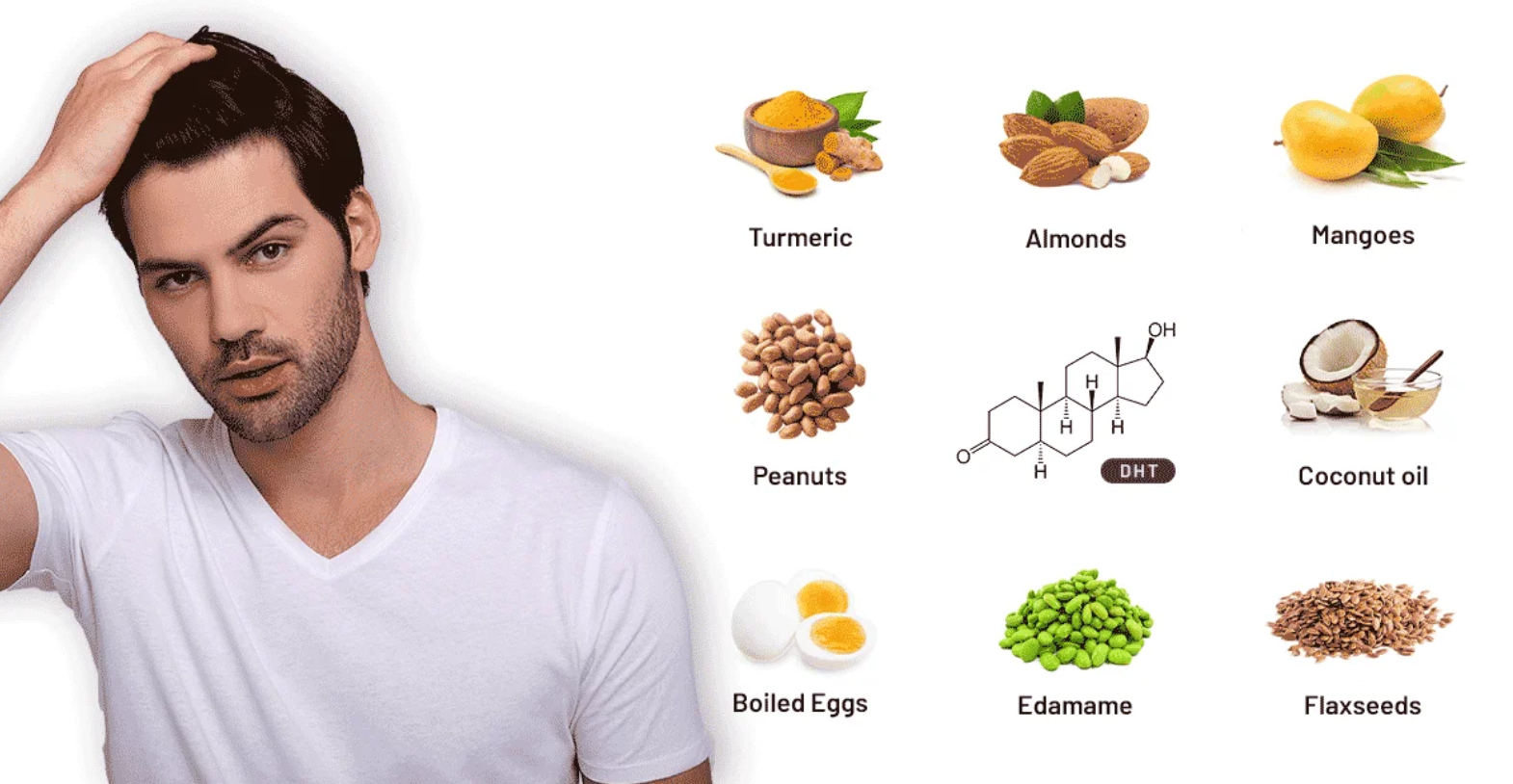
What is DHT Blocker
Understanding What is DHT Blocker
Explore various DHT blockers for hair loss treatment, including prescription medications like Finasteride and Dutasteride, natural foods and supplements such as pumpkin seed oil, green tea extract, and topical treatments. Understand their effectiveness, potential side effects, and how to choose the right option tailored to your needs. Always consult a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment regimen to ensure safety and maximum benefit. Note that DHT blockers may pose risks for fetal development, hence special precautions are advised. Individual response varies based on genetic, lifestyle, and overall health factors.
What is a DHT Blocker?

US Trichology Institute
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is an androgen hormone responsible for developing male secondary sexual characteristics during puberty. However, when present at higher concentrations later in life, DHT can shrink hair follicles and lead to pattern baldness or alopecia. To combat this issue, individuals often consider using DHT blockers to minimize hair fall and promote hair regrowth. We examines various DHT blocking solutions and explores their potential advantages and disadvantages.
- Prescription Medications
- Finasteride
- Dutasteride
- Natural Food and Supplements
- Pumpkin Seed Oil
- Green Tea Extract
- Pygeum Bark Extract
- Stinging Nettle Root Extract
- Topical Treatments
- Topical Finasteride
Prescription Medications
Two primary FDA approved drugs exist for combating hair loss caused by high DHT levels: Finasteride and Dutasteride. Both work by targeting the 5 alpha reductase enzyme, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). By obstructing this pathway, they effectively lower DHT levels within the body.
Finasteride
Finasteride comes in pill form, taken once daily, usually yielding positive results after three months of regular consumption. Its effects last only while actively taking the drug; discontinuation will allow DHT production to return gradually over time. Some possible side effects include decreased sex drive, erectile dysfunction, breast tenderness, and rash.
Key Points:
- Inhibits 5-alpha reductase type II enzyme
- Lowers serum and tissue DHT levels
- Effective for male and female pattern hair loss
Dutasteride
Though not specifically approved for hair loss treatment, Dutasteride has been employed off label due to its powerful impact on suppressing DHT synthesis via two distinct 5 alpha reductase isozymes types I and II. Research suggests that Dutasteride reduces DHT concentration by up to 93%, surpassing Finasteride’s 70% reduction rate. Nevertheless, long term risks remain uncertain, given limited data availability regarding adverse events related to prolonged utilization.
Key Points:
- Simultaneously targets 5 alpha reductase types I and II enzymes
- Potently lowers serum and tissue DHT levels
- Used primarily off label for hair loss treatment
What is The Best DHT Blocker: Natural Food and Supplements

How to Find Trichology Near Me
Various plant derived components have garnered attention for potentially acting as natural DHT blockers, offering less invasive alternatives to pharmaceuticals. While scientific evidence supports their capacity to restrict DHT formation, further investigation is necessary to substantiate claims fully. Here we delve into four prominent naturally occurring DHT blockers.
What is a Natural DHT Blocker
Best Certified Trichologist Milwaukee Wisconsin
Pumpkin Seed Oil
Research indicates that consuming pumpkin seed oil could increase hair count and decrease hair loss in males experiencing androgenetic alopecia. The active ingredient responsible for this effect appears to be delta 7 sterine, found abundantly in pumpkin seeds. Delta-7 sterine functions similarly to finasteride by hindering 5 alpha reductase activity, thus diminishing DHT production.
Key Points:
- Contains delta 7 sterine, a 5 alpha reductase inhibitor
- Increases hair count and decreases hair loss
- Available as dietary supplement or incorporated into shampoo and conditioner formulas
Green Tea Extract
EGCG (epigallocatechin gallate) the main polyphenolic compound in green tea exhibits antiandrogen properties, partially attributed to its ability to hinder 5 alpha reductase activity. One study demonstrated that mice fed EGCG experienced reduced DHT levels and slowed down the progression of skin disorders linked to excessive androgens. Human trials evaluating EGCG’s role in managing hair loss are ongoing.
Key Points:
- Rich source of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG)
- Possesses antiandrogen properties, including 5 alpha reductase inhibition
- Further clinical investigations needed to determine effectiveness in humans
Pygeum Bark Extract
Extract derived from the bark of Prunus Africana trees contains triterpenoid constituents believed to impede 5 alpha reductase function, subsequently limiting DHT biosynthesis. A systematic review analyzing eight randomized controlled trials concluded that pygeum bark extract improved urinary symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia, suggesting its potential utility in mitigating DHT induced conditions.
Key Points:
- Derived from Prunus Africana tree bark
- Comprises triterpenoid elements capable of inhibiting 5 alpha reductase
- Demonstrated improvement in urinary symptoms linked to benign prostatic hyperplasia
Stinging Nettle Root Extract
Stinging nettle root extract harbors phytochemicals known as lignans, particularly secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG), credited with blocking DHT binding sites on androgen receptors. Consequently, SDG prevents DHT from initiating harmful reactions leading to hair miniaturization and eventual hair loss. Nonetheless, additional human studies need to validate these findings conclusively.
Key Points:
- Contains lignans, notably secoisolariciresinol diglucoside (SDG)
- Occupies DHT binding sites on androgen receptors, averting deleterious interactions
- Requires further human trials to corroborate claimed benefits
Topical Treatments
Applying topical solutions containing DHT blockers directly onto affected areas offers an alternative method for minimizing DHT influence locally without exposing users to systemic consequences inherent in oral medications. Among them, topical finasteride emerges as a promising candidate warranting deeper exploration.
Topical Finasteride
In contrast to conventional finasteride tablets, topically administered finasteride provides targeted delivery, circumventing general absorption throughout the body. Preliminary research implies that topical finasteride retards hair thinning and fosters regrowth comparable to oral counterparts yet with fewer reported side effects. Notably, females contemplating DHT blockers for hair loss should seek advice from a hair loss specialist due to heightened safety concerns surrounding oral DHT blockers in women.
Key Points:
- Offers direct application onto affected regions
- Reduces reliance on systemic distribution
- Comparable efficacy to oral finasteride with potentially lower incidence of adverse effects
Choosing the Best DHT Blocker
Selecting the ideal DHT blocker necessitates weighing multiple factors, including personal preference, medical history, cost, and expected outcomes. Individuals must assess their priorities carefully and engage in open dialogue with healthcare professionals to make informed decisions aligned with their wellbeing objectives. Below is a summary checklist outlining critical aspects worth pondering prior to commencing any novel therapeutic intervention.
Before Starting Any New DHT Treatment Regimen
-
Discuss your intentions with a trusted healthcare provider
-
Review current medications and underlying health issues
-
Evaluate costs and insurance coverage details
-
Set realistic expectations regarding timelines and achievable gains
-
Monitor progress regularly through follow-ups with clinicians
-
Document changes observed during treatment periods
By following this comprehensive guide, you can navigate the complex landscape of DHT blockers confidently and select the most suitable option tailored to your needs. Remember always to consult a qualified healthcare practitioner before embarking on any new therapies to safeguard your health and optimize outcomes.
DHT Blockers for Women: An Informative Guide
Hair loss affects millions of women worldwide, with many seeking effective treatments to address the problem. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone, plays a vital role in causing hair loss in both men and women. Therefore, blocking DHT production can help slow down or even reverse hair loss. Several DHT blockers are available, but their suitability and safety differ for women compared to men. Let us explore various DHT blockers, focusing on those appropriate for women.
Prescription Medication Finasteride
Finasteride is a widely recognized DHT blocker, typically sold under brand names Proscar and Propecia. Initially developed to treat benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH), researchers discovered its beneficial effects on hair restoration. Though Finasteride blocks DHT efficiently, it carries potential risks for fetal development, contraindicating its use in pregnant women or those planning pregnancy.
-
How does Finasteride work?
- Finasteride inhibits Type II 5α-reductase, an enzyme responsible for transforming testosterone into DHT. Lowering DHT levels helps restore normal hair growth patterns.
- Benefits for women
- Slows down hair loss
- Promotes new hair growth
- Risks and Precautions
- Cannot take if pregnant or planning pregnancy due to risk of birth defects
- May cause side effects such as decreased libido, depression, and mood swings
- Regular monitoring of liver function tests required
Over the Counter Options Saw Palmetto Hair Loss
Saw Palmetto, extracted from Serenoa repens berries, has gained popularity as a natural DHT blocker. It acts similarly to Finasteride by inhibiting 5α reductase, resulting in lower DHT levels. Unlike Finasteride, however, Saw Palmetto doesn’t pose severe risks to fetal development, rendering it safer for women, especially those who wish to conceive.
-
How does Saw Palmetto work?
- Like Finasteride, Saw Palmetto inhibits Type II 5α-reductase, thereby reducing DHT levels.
- Benefits for women
- Can slow down hair loss
- Could encourage new hair growth
- Generally considered safe for premenopausal women
- Side Effects
- Relatively mild side effects, such as stomach upset, nausea, and headaches
Herbal Remedy Green Tea Extract
Green tea extract, rich in antioxidants, has shown promise in treating hair loss. Studies indicate that green tea catechins can limit 5α reductase activation, thus reducing DHT levels and promoting hair growth.
-
How does Green Tea Extract work?
- Epigallocatechin Gallate (ECGC), a component of green tea extract, inhibits Type II and III 5α-reductase.
- Benefits for women
- Slows down hair loss
- Encourages new hair growth
- Antioxidant protection for overall hair health
- Considerations
- Consuming moderate amounts of green tea is likely safe; however, concentrated extracts require caution.
Spironolactone for Hair Loss
Spironolactone, initially designed as a diuretic and hypertension medication, demonstrates anti-androgenic effects, making it useful for treating hair loss. It indirectly lowers DHT production by blocking androgen receptors. Due to spironolactone’s mechanism of action, it poses teratogenic risks similar to Finasteride, advising against its use during pregnancy.
-
How does Spironolactone work?
- Spironolactone competitively binds to androgen receptors, preventing DHT attachment and subsequent signaling.
-
Benefits for women
- Decreases hair loss
- Enhances new hair growth
-
Risks and Precautions – Spironolactone Side Effects
- Teratogenicity concerns analogous to Finasteride
- Menstrual irregularities, breast tenderness, and fatigue may occur
Women suffering from hair loss can find relief in various DHT blockers, ranging from prescriptions to herbal remedies. When choosing a suitable DHT blocker, understanding each product’s mechanisms, benefits, and potential drawbacks is imperative. As previously noted, DHT blockers may entail risks for fetal development. Thus, special precautions apply to women of childbearing age. Ultimately, engaging in thorough discussions with healthcare providers ensures the selection of an appropriate, efficient, and safe solution catering to each woman’s unique circumstances and requirements.
Unraveling the Mystery: What Does a DHT Blocker Do?
Best Certified Trichologist Rochester NY
Pattern hair loss impacts countless individuals globally, affecting self-esteem and quality of life. Various factors contribute to hair loss, among which dihydrotestosterone (DHT) assumes a predominant role. DHT blockers emerge as a viable solution aimed at curbing hair loss and enhancing hair density. But what exactly does a DHT blocker do? We dive deep into the intricate world of DHT and reveal the actions behind these remarkable agents.
DHT and Hair Loss
To comprehend the significance of DHT blockers, grasping the relationship between DHT and hair loss becomes paramount. Testosterone metabolizes into DHT via the 5α-Reductase enzyme, triggering biological responses that affect hair follicles. High DHT levels induce hair cycle alteration, ultimately contributing to hair loss.
- Role of DHT in Hair Loss
- Binding to androgen receptors, DHT instigates cellular signals influencing the hair cycle
- Shortening anagen phase duration and extending telogen phase length
- Gradually miniaturizing hair follicles and transitioning terminal hairs into vellus ones
Mechanisms of Action
DHT blockers operate by interfering with either the synthesis or interaction stages of DHT, neutralizing its detrimental influences on hair growth. Two major modes of operation characterize DHT blockers: inhibiting 5α-Reductase and occupying Androgen Receptor Sites.
Inhibiting 5α Reductase
The first category includes molecules thwarting the creation of DHT by restraining the catalytic action of 5α-Reductase. Such agents consist mainly of synthetic chemicals and botanical extracts.
- Synthetic Compounds
- Finasteride, renowned for its robust 5α-Reductase suppression capabilities, is frequently prescribed for hair loss management.
- Works primarily by inhibiting Type II and partly Type III 5α-Reductase isoforms
- Noticeable improvements appear within six months of continuous use
- Side effects, though rare, involve decreased libido, ejaculation problems, and gynecomastia
- Dutasteride shares structural homology with Finasteride but boasts broader inhibitory spectrum across all five 5α-Reductase isoforms
- Typically utilized off-label for hair loss therapy
- Efficiency eclipses Finasteride in terms of DHT reduction rates
- Adverse effects mirror those seen with Finasteride, along with an elevated risk of persistent sexual dysfunctions
- Finasteride, renowned for its robust 5α-Reductase suppression capabilities, is frequently prescribed for hair loss management.
- Botanical Extracts
- Phytosterols, prevalent in numerous plants, exhibit competitive inhibition towards 5α-Reductase
- Includes beta-sitosterol, campesterol, stigmasterol, brassicasterol, and sitostanol
- Primarily hamper Type I and II 5α-Reductase isoenzymes
- Limited bioavailability challenges full exploitation of their DHT-lowering abilities
- Phytosterols, prevalent in numerous plants, exhibit competitive inhibition towards 5α-Reductase
Occupying Androgen Receptor Sites
Alternately, DHT blockers act upon the androgen receptors themselves, denying access to DHT and other androgens. Antiandrogens constitute the second group, comprised chiefly of nonsteroidal and steroidal entities.
- Nonsteroidal Agents
- Flutamide serves as a versatile androgen receptor antagonist, impairing DHT binding efficiency
- Mostly prescribed for advanced prostate cancer cases
- Rarely indicated solely for hair loss owing to hepatotoxicity fears
- Cyproterone Acetate excels at obstructing androgen receptors, displaying marked affinity toward glucocorticoids and progestogens
- Applied principally in Europe for treating acne and hair loss
- Infrequent usage due to unfavorable side effect profiles
- Flutamide serves as a versatile androgen receptor antagonist, impairing DHT binding efficiency
- Steroidal Entities
- Spironolactone possesses weak androgen receptor antagonistic attributes coupled with intrinsic progestational qualities
- Often deployed for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)-related hair loss
- Commonplace utilization amongst female populations because of minimal masculinizing effects
- Spironolactone possesses weak androgen receptor antagonistic attributes coupled with intrinsic progestational qualities
What is DHT Blocker for Hair?
Combining different classes of DHT blockers amplifies their respective strengths while simultaneously attenuating potential weaknesses. Joint efforts prove valuable for patients resistant to monotherapy or enduring pronounced adverse effects.
- Synergistic Approach
- Merging DHT synthesis inhibitors alongside androgen receptor antagonists produces complementary cascades
- Reinforcing total DHT sequestration while preserving physiological homeostasis
- Mitigating undesirable side effects by employing lower dosages of individual components
- Merging DHT synthesis inhibitors alongside androgen receptor antagonists produces complementary cascades
What Does a DHT Blocker Do?
A DHT blocker intervenes in the multifarious processes governing hair cycling and androgenic interactions, presenting hopeful prospects for those battling hair loss. From impeding 5α-Reductase enzymatic activities to occupying androgen receptor docking stations, DHT blockers demonstrate immense potential in restoring lost confidence alongside receding locks. Delving beneath superficial appearances reveals a myriad of molecular machinations working tirelessly to preserve our crowning glory. With continued advancements in research and technology, future developments hold incredible promises for individuals grappling with the burgeoning challenge of hair loss.
How Long Does DHT Blocker Take to Work
DHT blocker to work may depend on the specific type being used. For instance, Finasteride, a commonly prescribed DHT blocker tablet, can take from three to six months before any effect is noticed. This is true even if taken daily. However, it should be noted that the effects of these drugs may not be permanent and could revert if the prescription is stopped. Furthermore, they may not be suitable for women of reproductive age. Different forms of DHT blockers may have varied durations until noticeable effects become apparent. As always, consulting a healthcare professional before starting any new treatment regimen is crucial to ensuring safety and maximizing the likelihood of success.
How to Find Trichology Near Me
